WEDNESDAY, MAY 23, 2018: NOTE TO FILE

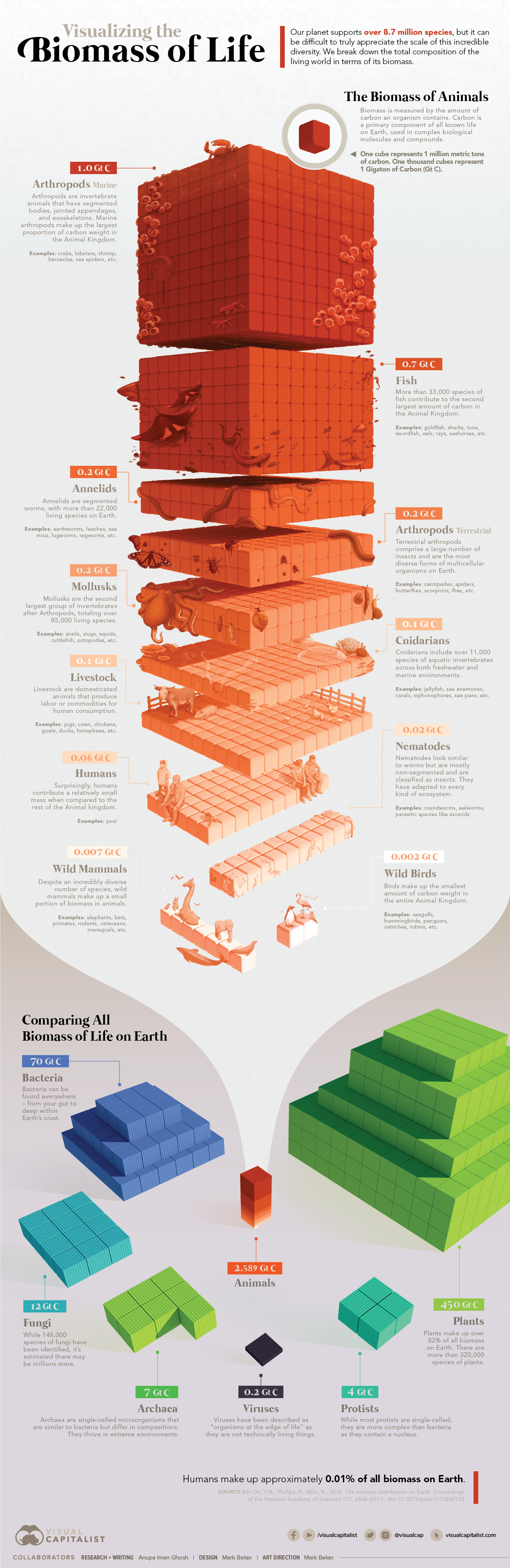
Earth's Biomass
Species/local-population extinction is one measure of Anthropocene progress, but biomass change is another
Eric Lee, A-SOCIATED PRESS
TOPICS: TEMPORAL BLINDNESS, FROM THE WIRES, THE BEAT GOES ON
Abstract: The conversion of Earth's biomass into pets, livestock, and humans is not page one news for some reason. That only 4 percent of mammalian biomass is wild fails to seem like it matters. Oh, but because of humans mammalian biomass is now so much higher, so....Anthropocene enthusiasts are missing something.
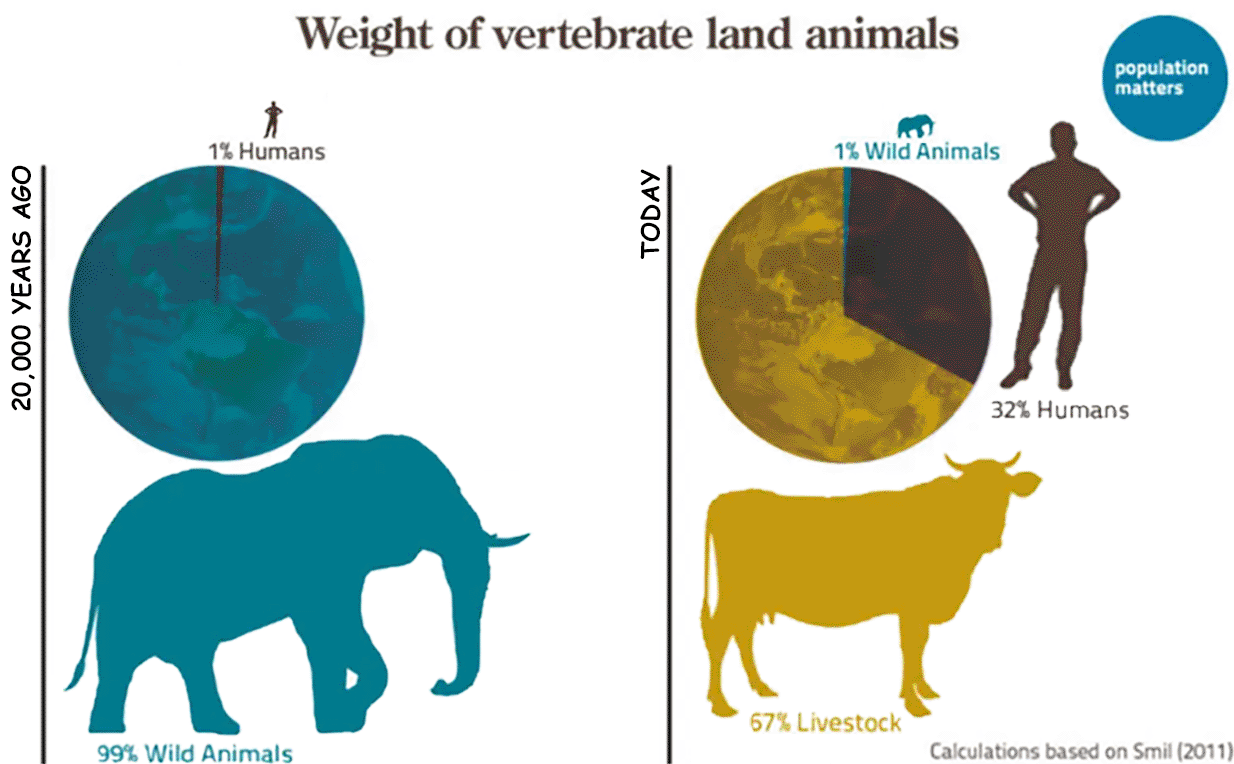
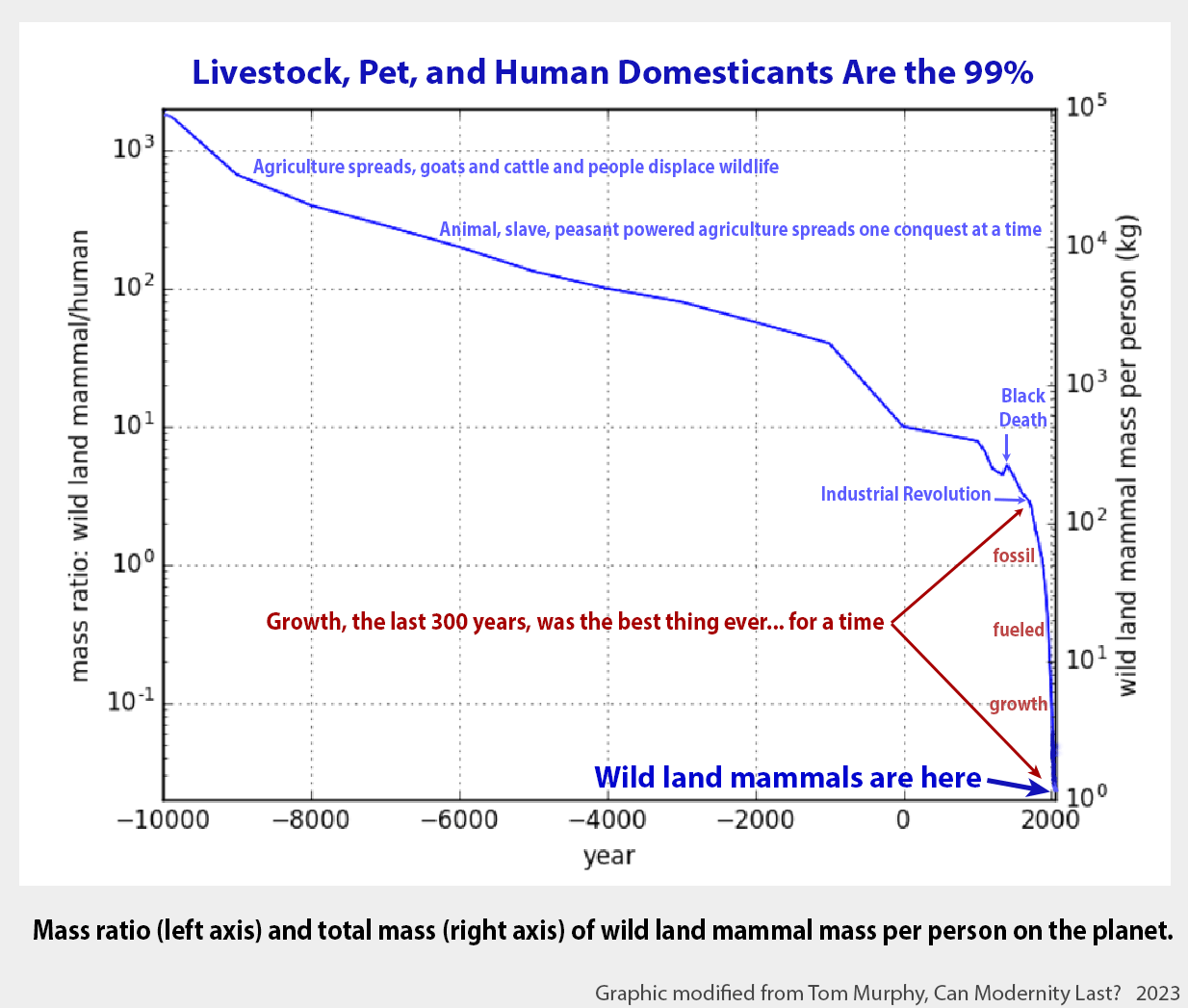
TUCSON (A-P) — In the 21st Century humans amount to 0.01% of Earth's biomass, up from 0.00008% 10,000 years ago.
| Gt C giga tons carbon |
Percent of Biomass sans deep subsurface/fiber |
Human equivalents hu-mans (hu=1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.06 | 0.01% hu-mans | 1 hu |
| 0.06 | 0.01% viruses | 1 hu |
| 1 | 0.6% archaea | 60 hu |
| 2 | 1.1% animals | 110 hu |
| 4 | 2.2% protists | 220 hu |
| 9 | 5.1% bacteria | 510 hu |
| 12 | 6.7% fungi | 670 hu |
| 150 | 84% plants | 8,400 hu |
Global living biomass distribution. Absolute living biomass abundances of different taxa represented in a Voronoi diagram, with the area of each cell being proportional to that taxa global biomass. The specific shape of each cell has no meaning. For plants, the biomass of stems and tree-trunks are excluded, as it is mostly composed of non-living lignified tissue. For prokaryotes and viruses, deep subsurface biomass excluded as the prokaryotes in those environments are metabolically “dormant” |
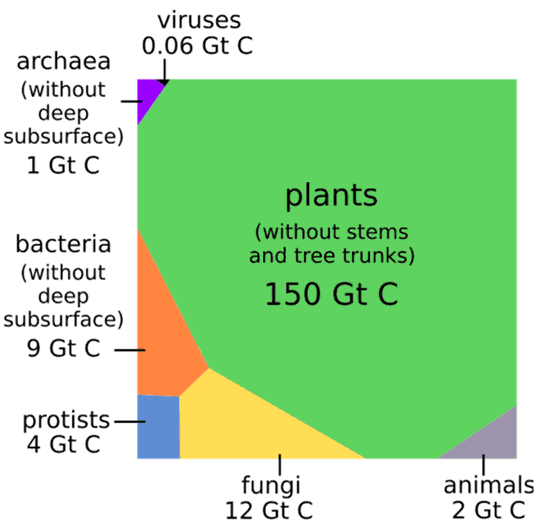 |
If bacteria and archaea living (slowly) in Earth's crust are included, they and their surface brethren total 78 Gt C, 13% of Earth's biomass, second only to plants in total biomass. And if "non-living" though essential stems and trunks of plants are added, plants weigh in at 450 Gt C. |
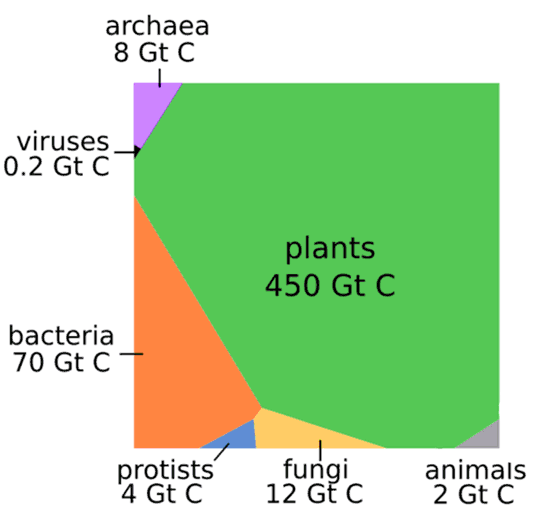 |
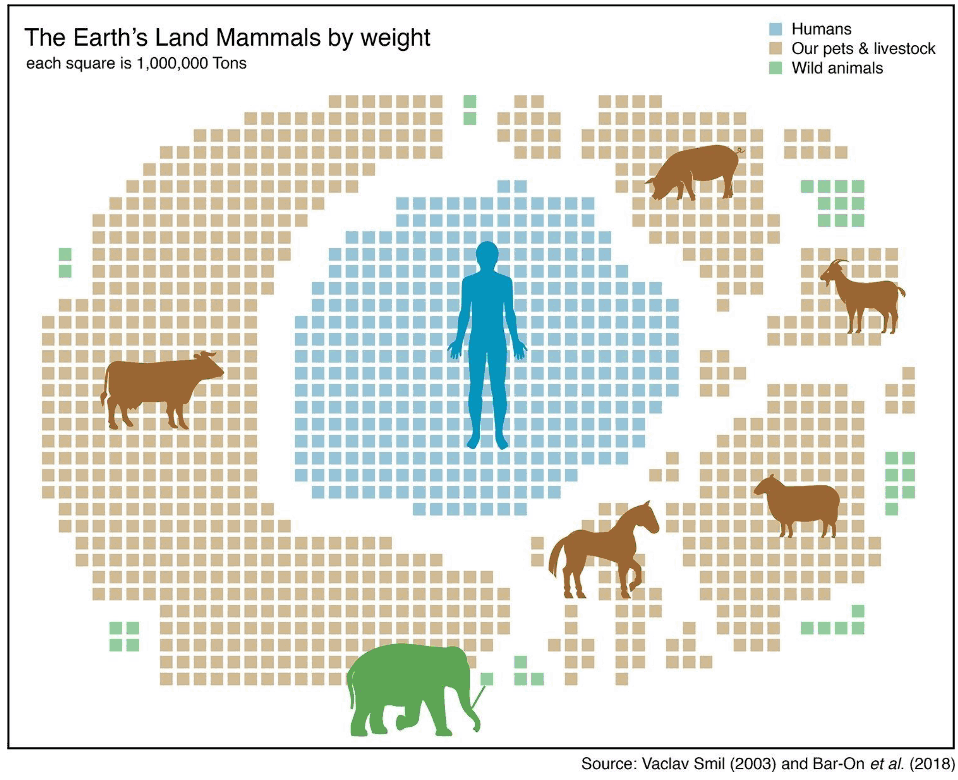
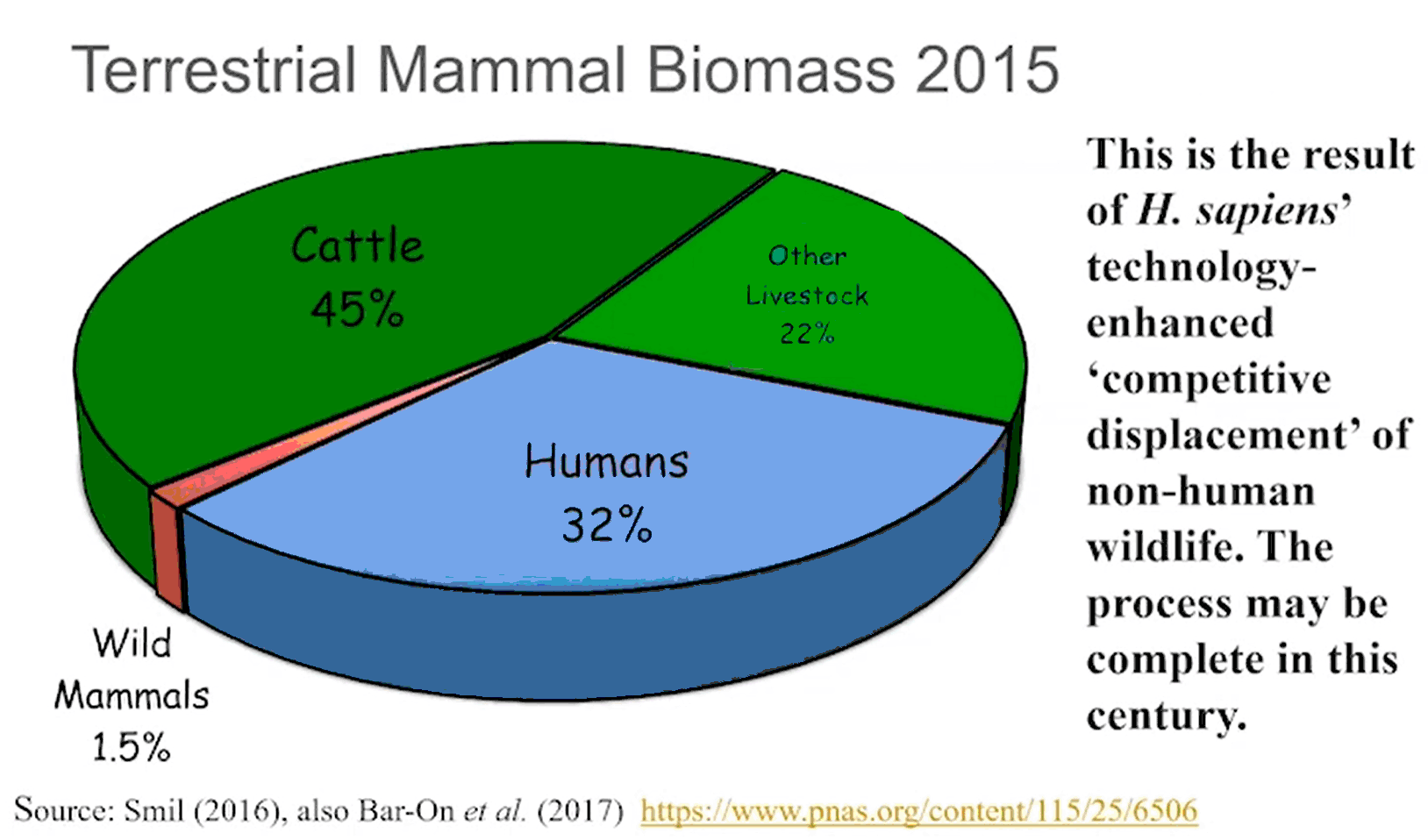
Absolute biomass of different animal taxa. Related groups such as vertebrates are located next to each other. The contribution of reptiles and amphibians to the total animal biomass is negligible. Animal biomass has changed in the past 10,000 years. Of all birds on the planet, 70 percent are now domestic poultry, mostly chickens. Most livestock are mammals who are now consumming much more of the planet's primary productivity to support the human population while only four percent are wild mammals. We are currently turning more fish into human biomass and the UN has called upon all to eat more arthropods/insects. And then what? If clever ape scientists/technologists figure out how to turn granite into food, we can keep growing the economy (to reduce poverty of course) for a few hundred years more. And then what? Well, if we convert the resources of the solar system into a Dyson sphere using all the energy output of Sol.... |
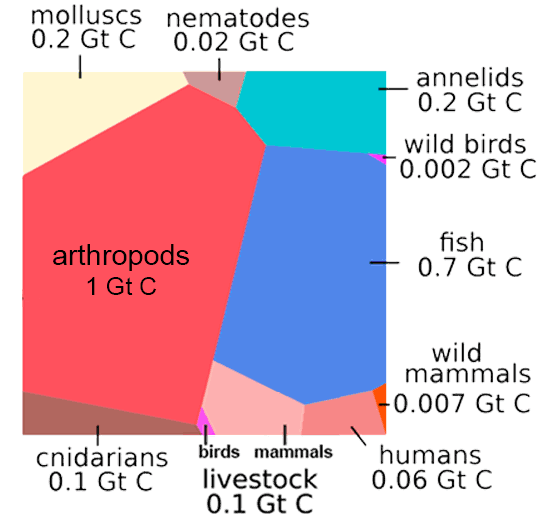 |
So plants, primary producers that almost all other surface life depends on, are 8,400 times more massive than humans even though we have reduced the plant biomass (via deforestation/agriculture) by 50% in celebration of the Anthropocene era climaxing in the 21st century.
| Gt C giga tons carbon |
Percent of Animal Biomass | Human equivalents hu-mans (hu=1) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.002 wild birds | 0.09% | 0.03 hu |
| 0.005 domestic birds | 0.21% | 0.08 hu |
| 0.007 wild mammals | 0.32% | 0.12 hu |
| 0.02 nemotodes | 0.9% | 0.33 hu |
| 0.06 humans | 2.7% of all animal biomass | 1 hu |
| 0.1 livestock | 4.6% | 1.7 hu |
| 0.1 cnidarians (jellyfish etc) | 4.6% | 1.7 hu |
| 0.2 annelids (worms) | 9.1% | 3.3 hu |
| 0.7 fish | 32.0% | 11.7 hu |
| 1.0 arthropods (insects etc) | 45.7% | 16.7 hu |
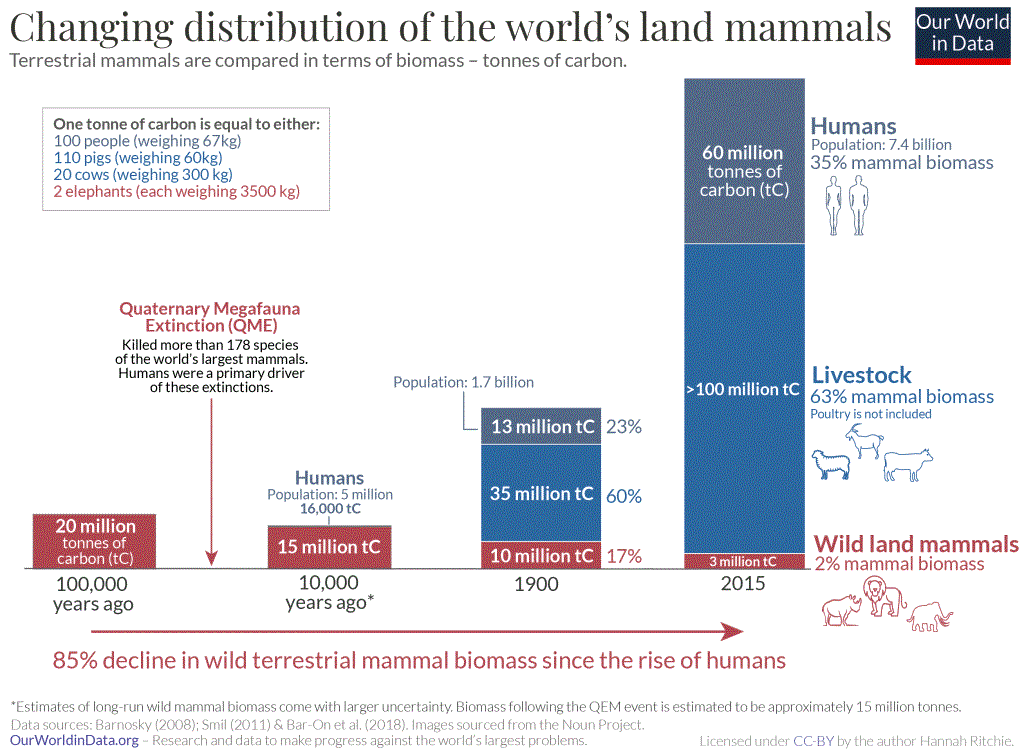
Humans, about 7 percent of all vertebrate biomass, are one species; livestock are a few species, mostly mammals, and all the other taxa are many species. While only 30 percent of all birds are currently wild, 10,000 years ago there were 25 times more wild birds than humans by weight. Now, for a time, there are 30 times more humans than wild birds by weight. These numbers will change in the near future (as measured in geological/ecolate time). In just a few millennia human biomass has increased 750 fold.
Hu-mans have also reduced the biomass of wild mammals by 83 percent although the overall biomass of mammals has increased over fourfold (414%), proof that hu-mans are far superior (or not). Some (but not all) wild mammals that do not go extinct will end up in zoos to amuse, and will still be called 'wild' as the zoos will become evermore natural looking. You can't stop progress (but Nature can).
Source: PNAS. For more graphics: The Guardian. Important details in the Appendix. High functioning nerds read SlashDot: News for Nerds, and when it comes to ecolate topics many clearly 'don't know enough to have an opinion' and are too cognitively limited to realize they don't know enough as evidenced by the comments of some. |
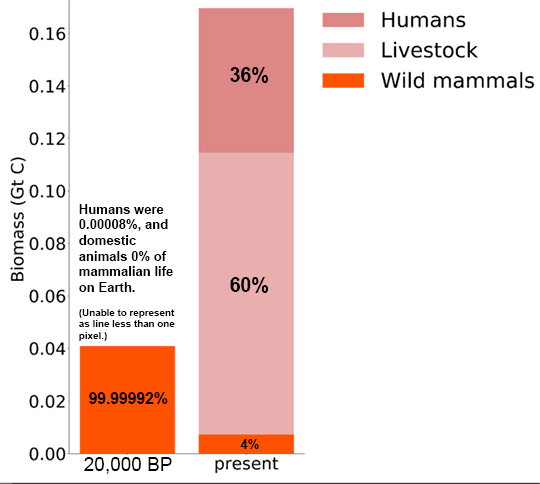 |
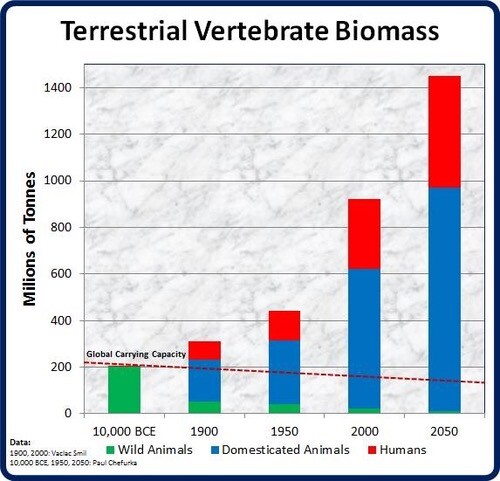
A perhaps surprising fact is that most life on earth is terrestrial, only about one percent lives in the water world that makes up 71% of the planet's surface, less than lives in the deep subsurface beneath the waters of the world. About 0.3% of industrially produced human food (calories) comes from aquatic sources. Presumably the vast ocean of phytoplanton is as productive as can be given that water captures much of the solar energy, supporting a less vast number of zooplanton that minimize it's population. The zooplanton is then food for multiple levels of longer lived predatious animals whose biomass exceeds that of the phytoplanton that supports the ocean's non-photosyntheic organisms having five times the carbon mass. The biomass of the primary producers is small as they are small and reproduce quickly to be eaten by consummers. Industrial fishing is a late development, so only 15% of fish biomass has been consummed, but humans are working hard, enabled by currently abundant fossil fuels, to do to wild fish what has already been done to wild mammals.
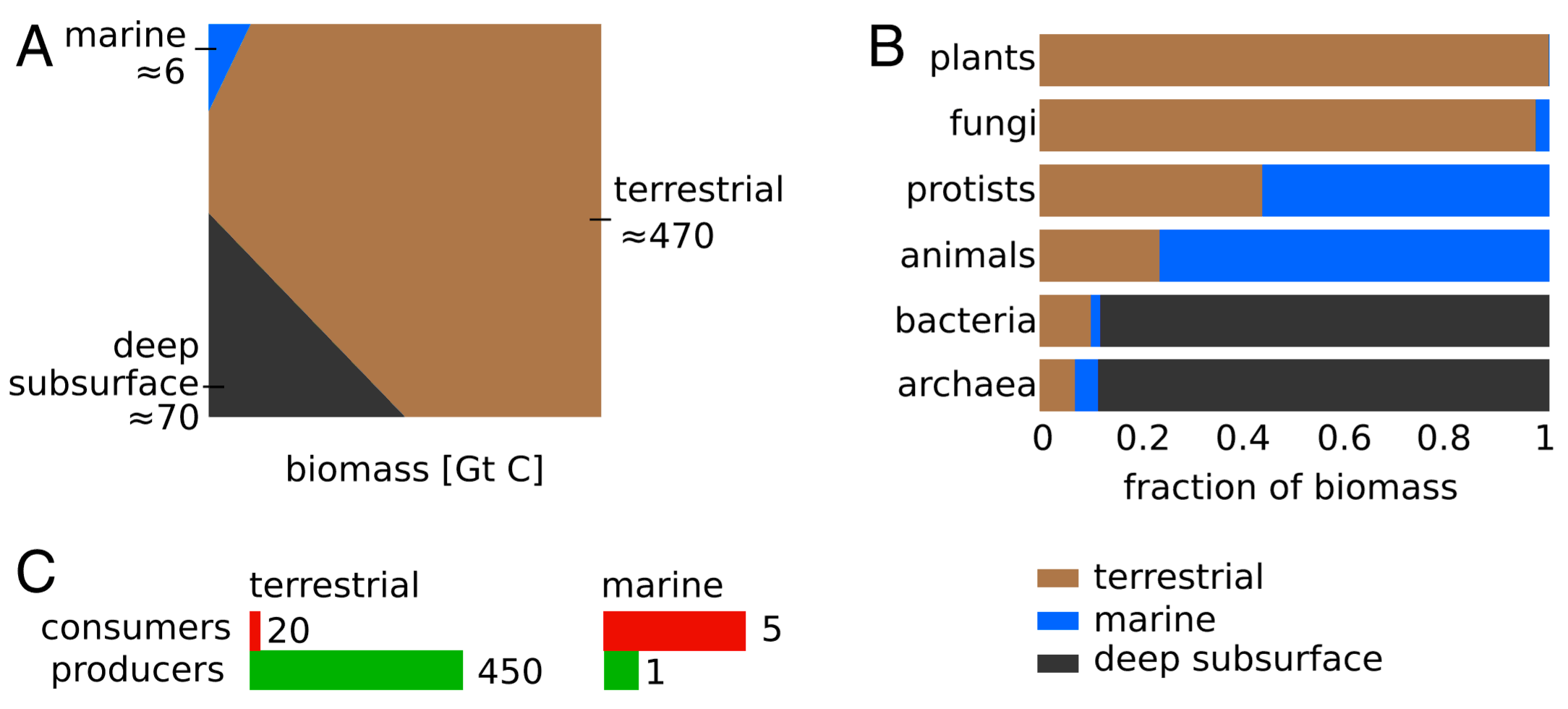
A recent visualization: